Cshell
Summer 2022
Tools:

The project is a part of Operating Systems I CMPT300 at Simon Fraser
University. It involves creating a simple command-line interpreter
or shell, dubbed cshell, that supports environment variables and a
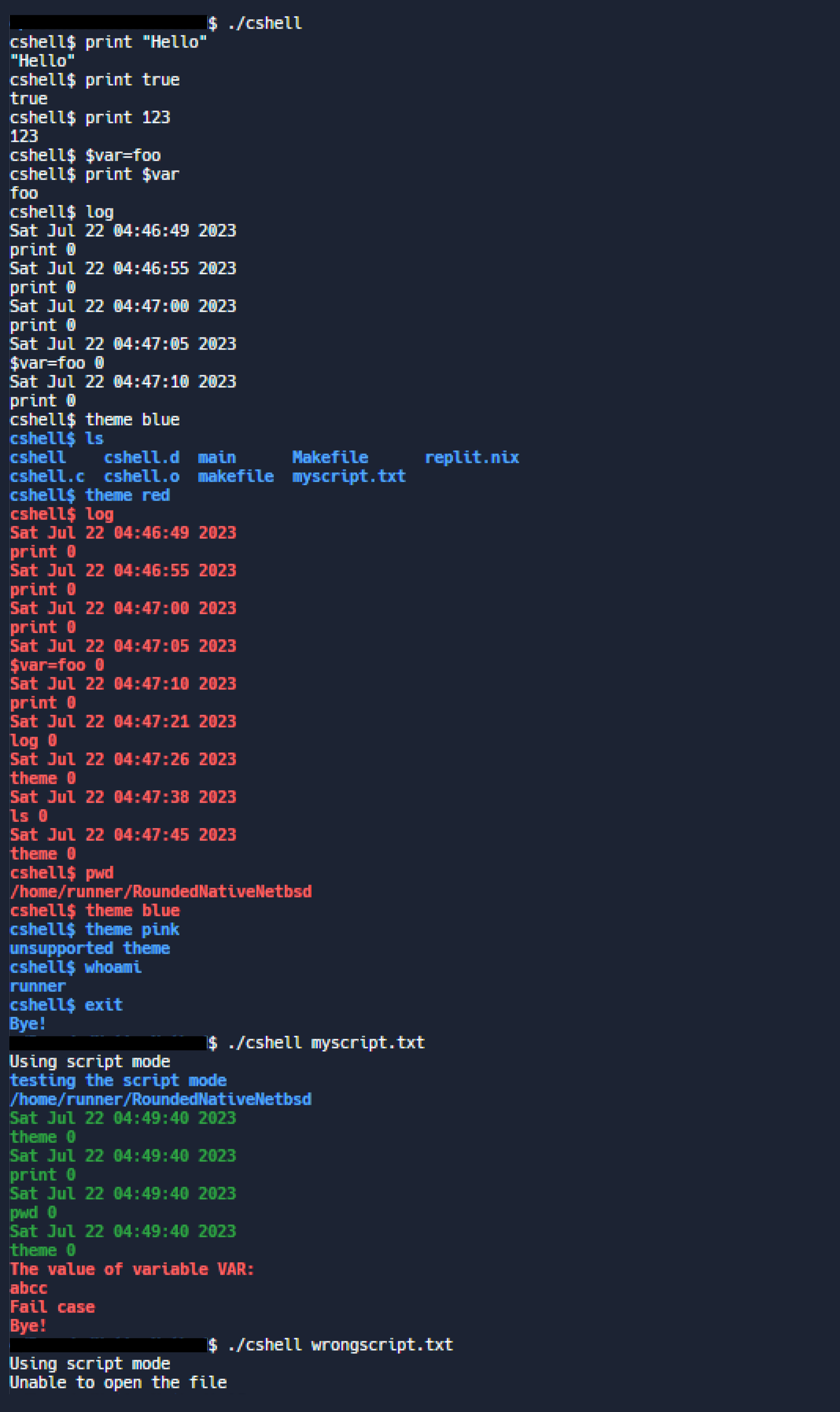
history of executed commands. The cshell performs in two modes:
interactive and script.
Key features of this shell include:
1. Command Logging: The shell maintains a log of all commands
executed, including their names, timestamps, and exit codes. It can
print these logs upon the user's request, and it can clear the logs
when necessary. The command logging feature is achieved by using dynamic
memory allocation to maintain a flexible, scalable record of all
executed commands.
2. Environment Variables Management: The shell can handle custom
environment variables. Users can create new environment variables,
modify existing ones, and retrieve their values. The project implements
these features by maintaining a dynamic array of environment variables,
each represented by a struct holding the variable's name and value.
3. Built-in Commands Handling: The shell supports a number of
built-in commands like "exit", "log", "print", and "theme". The handling
of these commands is embedded directly within the shell program itself,
providing rapid and efficient execution.
4. Non-built-in Commands Handling: In addition to built-in
commands, the shell is designed to execute any external, non-built-in
commands. Non-built-in commands like 'ls', 'pwd', and 'whoami' are executed in a
child process created by the 'fork()' system call. The 'exec()' system
call then executes the user's command in this child process, and the
'wait()' system call makes the shell wait for the child process to
terminate before proceeding.
5. Command Line Parsing: The shell can parse user input into distinct
command arguments, enabling it to handle commands with multiple
parameters.
6. Script Mode and Interactive Mode:Interactive mode prompts the user to enter commands, which are then
executed individually. Script mode reads and executes commands from a
pre-written script file. The shell handles both built-in and non-built-in
commands. The built-in commands include 'exit' (terminates the shell),
'log' (displays command history), 'print' (prints arguments given to
the command), and 'theme' (changes the color of the shell output).
7. Theming: The shell provides users with the option to change the
output theme colors to red, green, or blue, enhancing the user experience.
The shell program combines these features to provide a versatile and customizable
user interface for command execution. The project exhibits the efficient use of
dynamic memory management, process control, and system-level I/O operations in C.
